Xenix IBM PC v1.0 Exploration: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Setting up our VM = | == Setting up our VM == | ||
This specific version of Xenix is apparently only for the IBM PC AT, which uses a 80286. Let's first set up a VM for this, I'll be using [https://86box.net/ 86Box]. | This specific version of Xenix is apparently only for the IBM PC AT, which uses a 80286. Let's first set up a VM for this, I'll be using [https://86box.net/ 86Box]. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
! Floppy disks | ! Floppy disks | ||
| | | | ||
* '''Floppy drive(s):''' One 5.25" 1.2MB drive | * '''Floppy drive(s):''' One 5.25" 1.2MB drive (A:), one 5.25" 360K drive (B:) | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
That's all I have to say really -- SETUP is easy to follow along, so just follow along I guess. When it's done, remove the diskette. | That's all I have to say really -- SETUP is easy to follow along, so just follow along I guess. When it's done, remove the diskette. | ||
= Setting up Xenix = | == Setting up Xenix == | ||
If you want to download this version, please check it out on [https://winworldpc.com/product/xenix/ibm-pc-100 WinWorld]. | If you want to download this version, please check it out on [https://winworldpc.com/product/xenix/ibm-pc-100 WinWorld]. | ||
Now, back on topic. We'll install Xenix now | Now, back on topic. We'll install Xenix now. | ||
First, insert the BOOT diskette. Then, type 'fd /etc/badtrack'. Once that is done, boot the Xenix kernel by entering 'fd /xenix.fd' (not /xenix, /xenix.fd) | First, insert the BOOT diskette. Then, type 'fd /etc/badtrack'. Once that is done, boot the Xenix kernel by entering 'fd /xenix.fd' (not /xenix, /xenix.fd) | ||
Now, let's set up the hard disk. Simply type hdinit, and follow along. If it asks you how Xenix should be set up on the hard drive, just say that | |||
Xenix should take up all the space on the hard disk. It will erase the hard drive and copy some basic utilities onto there. Then, remove the floppy and boot into the hard disk once it | |||
has been finished. | |||
Now, type 'xinstall base'. Insert the base floppies. This will install the base system. The script doesn't really check the product type, so you can use | Now, type 'xinstall base'. Insert the base floppies. This will install the base system. The script doesn't really check the product type, so you can use | ||
the same command but different floppies -- like you can use 'xinstall base' but insert the SDK floppies to install the SDK. | the same command but different floppies -- like you can use 'xinstall base' but insert the bundled SDK floppies to install the bundled SDK. | ||
That's really about it when installing Xenix. Once the installation is done, you can remove the floppies and boot into the hard drive. However, | That's really about it when installing Xenix. Once the installation is done, you can remove the floppies and boot into the hard drive. However, | ||
the only available user is root. You can add one later, however. | the only available user is root. You can add one later, however. | ||
Adding a user is simple. Once in the root account, just type 'mkuser' to create a user. Once you've logged into the user, you will get a welcome mail message. To read it, simply type 'mail'. | |||
To quit it, IIRC, you can type 'q'. Home directories are in the /usr folder. If you created a user by the name 'test', then it would be at /usr/test. | |||
More information may be in the manuals, which are available at [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/sco/pc_xenix/ Bitsavers]. | |||
== Developing software == | |||
=== For Xenix === | |||
[[File:xenixtarget.png|thumb|Compiling a small C application for Xenix, under Xenix]] | |||
I created a file named 'hello.c' using the following command: | |||
<pre>cat >> hello.c << EOF</pre> | |||
This will output the contents of stdin into hello.c until you give it the literal string EOF. | |||
And so, here is the source code of hello.c: | |||
<pre> | |||
main() { | |||
printf("hello, world!\n"); | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
Now, we compile it using <pre>cc hello.c -o hello</pre> | |||
And then, we simply run it! It gives out the message like we would've expected. | |||
There is also like you might've expected, a linker, by the name of ld -- and a lot of other things, too. There is yacc and lex | |||
included, and adb. Although, yacc might not be included in the included SDK. You might have to use the specific SDS, which can be found [https://winworldpc.com/product/xenix-development-system/100-ibm on WinWorld]. | |||
=== For DOS === | |||
[[File:dosxenix.png|thumb|Running a small C application for MS-DOS, compiled using Xenix]] | |||
Making a simple Hello World application in C for DOS is relatively simple. | |||
Say the source code posted above for compiling under Xenix is now in doshello.c, to compile it for DOS, you would use the following: | |||
<pre> | |||
cc doshello.c -dos -o doshello.exe | |||
</pre> | |||
Then, to copy doshello.exe to a already formatted disk, assuming you want to copy it to the equivalent of A: (/dev/fd0), use the following: | |||
<pre> | |||
doscp doshello.exe /dev/fd0:/doshello.exe | |||
</pre> | |||
You can also copy it to B: with /dev/fd1. | |||
Please keep in mind that, if you compile everything and do a link, the linker name is different for DOS, of course. The specific name | |||
is dosld. | |||
=== Makefile === | |||
Interestingly, there is a make implementation in the SDK. For the "hello, world!" application under Xenix, you can write this extremely simple Makefile: | |||
<pre> | |||
hello: hello.c | |||
cc hello.c -o hello | |||
</pre> | |||
and save it as simply 'Makefile'. Oh yeah, by the way, make sure those 4 spaces in front of 'cc hello.c' is actually a tab when you enter it in. | |||
And, for compiling the simple DOS "hello, world!": | |||
<pre> | |||
all: doshello.exe copy | |||
doshello.exe: doshello.c | |||
cc doshello.c -dos -o doshello.exe | |||
copy: doshello.c | |||
doscp doshello.exe /dev/fd0:/doshello.exe | |||
</pre> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:23, 21 July 2024
Setting up our VM
This specific version of Xenix is apparently only for the IBM PC AT, which uses a 80286. Let's first set up a VM for this, I'll be using 86Box.
I created a virtual machine with the following (stuff that I didn't mention were simply left blank):
| Setting type | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Machine |
|
| Display |
|
| Storage controllers |
|
| Hard disks |
|
| Floppy disks |
|
Using this configuration, try starting up the VM -- without any floppy disks in the drive, or anything like that. You might get a 161. It mentions to run SETUP.
How do you run SETUP, you may ask? IBM provided a diskette which would boot into special software that could configure your IBM AT. Luckily, people have archived this diskette -- it's available on WinWorld. Go ahead and download 2.07.
Then, insert the diskette. Simply continue where it said to run SETUP. It may ask you if you have finished connecting the battery. It'll throw a 0151. Press the Enter key a few times (there might be another way to bypass this error, but this is all I know). If you skip the time and date, it'll ask you to confirm -- press N and type the following:
For time, just use the current time.
For date, the current date, but replace the current year with 1985.
When it asks for a fixed disk, say that type 2 is installed -- if you used my 20MB disk configuration. This list is very useful for hard disk geometry when dealing with the IBM/PC AT.
That's all I have to say really -- SETUP is easy to follow along, so just follow along I guess. When it's done, remove the diskette.
Setting up Xenix
If you want to download this version, please check it out on WinWorld.
Now, back on topic. We'll install Xenix now.
First, insert the BOOT diskette. Then, type 'fd /etc/badtrack'. Once that is done, boot the Xenix kernel by entering 'fd /xenix.fd' (not /xenix, /xenix.fd)
Now, let's set up the hard disk. Simply type hdinit, and follow along. If it asks you how Xenix should be set up on the hard drive, just say that Xenix should take up all the space on the hard disk. It will erase the hard drive and copy some basic utilities onto there. Then, remove the floppy and boot into the hard disk once it has been finished.
Now, type 'xinstall base'. Insert the base floppies. This will install the base system. The script doesn't really check the product type, so you can use the same command but different floppies -- like you can use 'xinstall base' but insert the bundled SDK floppies to install the bundled SDK.
That's really about it when installing Xenix. Once the installation is done, you can remove the floppies and boot into the hard drive. However, the only available user is root. You can add one later, however.
Adding a user is simple. Once in the root account, just type 'mkuser' to create a user. Once you've logged into the user, you will get a welcome mail message. To read it, simply type 'mail'. To quit it, IIRC, you can type 'q'. Home directories are in the /usr folder. If you created a user by the name 'test', then it would be at /usr/test.
More information may be in the manuals, which are available at Bitsavers.
Developing software
For Xenix
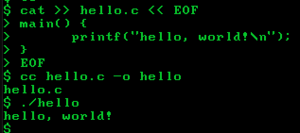
I created a file named 'hello.c' using the following command:
cat >> hello.c << EOF
This will output the contents of stdin into hello.c until you give it the literal string EOF.
And so, here is the source code of hello.c:
main() {
printf("hello, world!\n");
}
Now, we compile it using
cc hello.c -o hello
And then, we simply run it! It gives out the message like we would've expected.
There is also like you might've expected, a linker, by the name of ld -- and a lot of other things, too. There is yacc and lex included, and adb. Although, yacc might not be included in the included SDK. You might have to use the specific SDS, which can be found on WinWorld.
For DOS
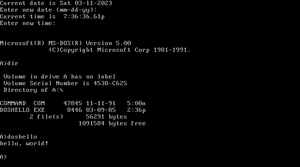
Making a simple Hello World application in C for DOS is relatively simple.
Say the source code posted above for compiling under Xenix is now in doshello.c, to compile it for DOS, you would use the following:
cc doshello.c -dos -o doshello.exe
Then, to copy doshello.exe to a already formatted disk, assuming you want to copy it to the equivalent of A: (/dev/fd0), use the following:
doscp doshello.exe /dev/fd0:/doshello.exe
You can also copy it to B: with /dev/fd1.
Please keep in mind that, if you compile everything and do a link, the linker name is different for DOS, of course. The specific name is dosld.
Makefile
Interestingly, there is a make implementation in the SDK. For the "hello, world!" application under Xenix, you can write this extremely simple Makefile:
hello: hello.c
cc hello.c -o hello
and save it as simply 'Makefile'. Oh yeah, by the way, make sure those 4 spaces in front of 'cc hello.c' is actually a tab when you enter it in.
And, for compiling the simple DOS "hello, world!":
all: doshello.exe copy
doshello.exe: doshello.c
cc doshello.c -dos -o doshello.exe
copy: doshello.c
doscp doshello.exe /dev/fd0:/doshello.exe